What Is the Best Description of Minute Ventilation
VC FRC IRV IRV ERV RV. Increasing respiratory rate or tidal volume will increase minute ventilation.

Influence Of Minute Ventilation On Breathing Frequency For Two Patients Download Scientific Diagram
Mechanical ventilation is used to assist or replace spontaneous breathing to reduce the work of breathing andor reverse life-threatening respiratory derangement in critically ill patients or to maintain respiratory function in those undergoing general anesthesia.

. Amount of oxygen needed by the body in 1 minute D. Alveolar ventilation is defined as respiratory minute volume or minute ventilation minus ventilation of the anatomic dead space. C The amount of air that is moved into and out of the lungs in 1 minute.
Similar to V D V T corrected minute ventilation was independently associated with hospital mortality in subjects with ARDS secondary to COVID-19. However it is a pressure controlled and time cycled mode which by definition is a pressure control mode. The amount of blood and the pressure at which it carries oxygen throughout the body C.
Unchanged because the minute ventilation does not change. At rest a normal person moves approximately a volume of 450 mL with each breath at a rate of 10 breathsmin so the minute ventilation is approximately 4500 mLmin. Therefore corrected minute ventilation can be a reliable assessment of the dead space which could.
Keep in mind the Minute Ventilation Minute Ventilation Lmin RR bmin x Tidal Volume liters If you decrease one or both the MV will be lower hypercapnia Tolerated in status asthmaticus and ARDSALI Called permissive hypercapnea. Alveolar ventilation is defined as respiratory minute volume or minute ventilation minus ventilation of the anatomic dead space 5. 3 Gas that can be forcibly expelled at the end of normal tidal expiration.
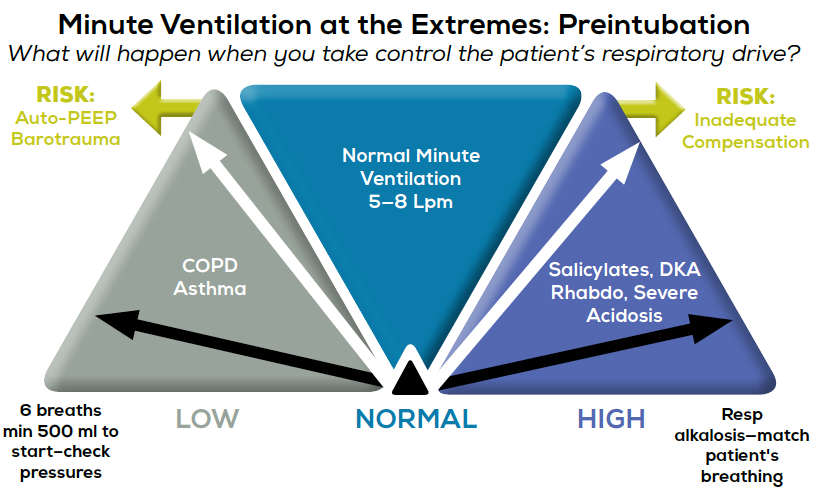
Normal minute ventilation is 5-8 litresmin Taxonomy. 1 Volume of gas inhaled during a breath 500ml baseline 2 Gas remaining after maximal expiration 15L determines by inward pressure of expiratory muscles and outward elastic recoil. For each breath the ventilator adjusts the driving pressure based on lung compliance and resistance to deliver target tidal volume.
Breaths are representative of ventilation over a minute. The ability of the red blood cells to offload oxygen to the cells of the body B. The respiratory rate and tidal volume determine a patients minute-ventilation.
The amount of air that is. Number of breaths a patient breathes in 1 minute Amount of air moved into and out of the lungs in 1 minute. B The amount of blood and the pressure at which it carries oxygen throughout the body.
If the patient was intubated primarily for hypoxemic respiratory failure then consider setting the rate just below the patients actual RR once theyre intubated. Dead space refers to airway volumes not participating in gas exchange. Corrected minute ventilation is a surrogate of V D V T that is easy to calculate at the bedside.
Minute ventilation rate and tidal volume Inspiratory gas flow Flow waveform Inspiratory to expiratory IE ratio Pressure limit. What is the best description of minute ventilation. Ideally watch the patient after intubation and adjust the RR until they are initiating a few breaths.
Minute ventilation is defined as the total volume of gas entering or leaving the lung per minute and is calculated as product of tidal volume and respiratory rate. In some series 10 breaths were used but the main point is that the value represents an estimate based on breathing that occurs for the most part in less than a minute unless of course the patient s respiratory rate was 8 breathsmin. However historically hypocapnia a very likely consequence of an increase in alveolar ventilation has been included as an essential feature of hyperventilation and alveolar hyperventilation 1 3 5.
The adequacy of the level of ventilation needs to be carefully monitored. Slow constant inspiratory flow rate IFR Constant IRF with end-inspiratory pause. Ventilation is a function of mechanics and intrinsic PEEP.
The disadvantage is that the ventilator may decrease support to a dyspneic patient because it cannot tell the difference between improving compliance and increasing inspiratory effort. D The ability of the body to exchange gases across the alveolar capillary membrane. Ventilator setting 1 is the best in terms of ABGs because it is the only setting that lowers the PCO 2.
What is the best description of minute ventilation. Volume controlled ventilation modified by. With DKA will need higher minute ventilation and greater Vt.
Since this setting violates the UIP but not the LIP patient is primarily at risk for barotrauma. Patients intubated for airway protection due to trauma or toxi-cology often do well with a normal minute-ventilation and as such initially setting respiratory rates at 1014 breathsminute and the tidal volume at. This is confusing because it does not.
Ventilation Primary goal of volume ventilation is the achieve a desired minute ventilation that matches the patients metabolic needs and accomplishes adequate gas exchange. A The ability of the red blood cells to offload oxygen to the cells of the body. E Which ventilator setting is best in terms of ABG results.
Chapter 8 What is the best description of minute ventilation. Amount of air move into and out of the lungs in one minute While completing some clinical time in the hospital for his EMT class an EMT student observed a patient being administered an IV fluid with a high oncotic pressure. Amount of air moved into and out of the lungs in 1 minute B.
Total milliliters of air moving into and out of the lungs in one breath C. Few patients have a respiratory rate of 8 breathsmin. The advantage is that minute ventilation is stabilized with varying respiratory system mechanics resistance compliance and inspiratory effort.
What is the best description of the ventilationperfusion VQ ratio. However historically hypocapnia a very likely conse-quence of an increase in alveolar ventilation has been included as an essential feature of hyperventilation and alveolar hyper-. Minute ventilation is the tidal volume times the respiratory rate usually 500 mL 12 breathsmin 6000 mLmin.

Carbon Dioxide And Oxygen Response Curves Deranged Physiology
Avoid Airway Catastrophes On The Extremes Of Minute Ventilation
No comments for "What Is the Best Description of Minute Ventilation"
Post a Comment